COMPACTION FACTOR TEST
AIM - To determine workability of concrete by compaction factor test.
APPARATUS - compaction factor apparatus, scoop, tamping rod, etc.
Theory - The compaction factor test is carried out to measure the degree of workability of fresh concrete with regard to the internal energy required for compacting the concrete thorough.
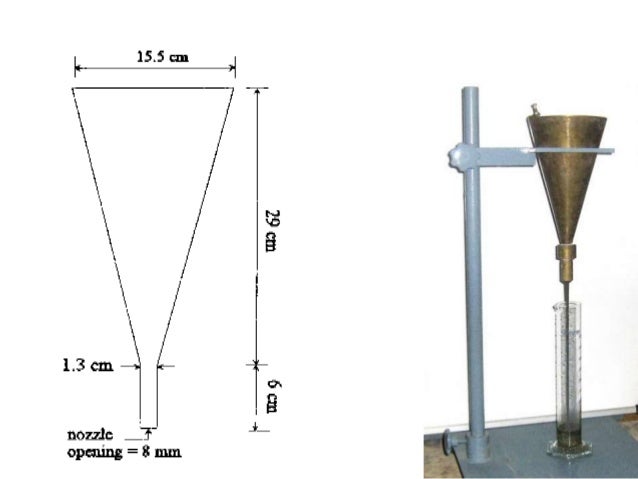
DIAGRAM -
AIM - To determine workability of concrete by compaction factor test.
APPARATUS - compaction factor apparatus, scoop, tamping rod, etc.
Theory - The compaction factor test is carried out to measure the degree of workability of fresh concrete with regard to the internal energy required for compacting the concrete thorough.
DIAGRAM -
Procedure-
1. place freshly prepared concrete in top mould before noting the mould of empty cylinder(W).
2. open trap door for mould 1. allow concrete to fall in 2nd mould
3.open trap for mould 3 allow concrete to fall in cylinder
4. remove excess concrete
5. note down the partially compacted concrete weight in cylinder after compaction (W1)
6. in same cylinder note down the weight of fully compacted concrete (W2)
7. W2-W/W1-W gives the compaction factor value indiacting the workability of fresh concrete